Storybook for React
You may have tried to use our quick start guide to setup your project for Storybook. If you want to set up Storybook manually, this is the guide for you.
This will also help you to understand how Storybook works.
Starter Guide React
Storybook has its own Webpack setup and a dev server. Webpack setup is very similar to Create React App, but allows you to configure it as you want.
In this guide, we will set up Storybook for your React project.
Table of contents
- Add @storybook/react
- Add react, react-dom, babel-core, and babel-loader
- Create the config file
- Write your stories
- Run your Storybook
Add @storybook/react
First of all, you need to add @storybook/react to your project. To do that, run:
npm i --save-dev @storybook/react
Add react, react-dom, babel-core, and babel-loader
Make sure that you have react, react-dom, babel-core, and babel-loader in your dependencies as well because we list these as peer dependencies:
npm i --save react react-dom
npm i --save-dev babel-core
npm i --save-dev babel-loader
Then add the following NPM script to your package.json in order to start the storybook later in this guide:
{
"scripts": {
"storybook": "start-storybook -p 9001 -c .storybook"
}
}
Create the config file
Storybook can be configured in several different ways.
That’s why we need a config directory. We’ve added a -c option to the above NPM script mentioning .storybook as the config directory.
For a basic Storybook configuration, the only thing you need to do is tell Storybook where to find stories.
To do that, create a file at .storybook/config.js with the following content:
import { configure } from '@storybook/react';
function loadStories() {
require('../stories/index.js');
// You can require as many stories as you need.
}
configure(loadStories, module);
That’ll load stories in ../stories/index.js.
Just like that, you can load stories from wherever you want to.
Write your stories
Now you can write some stories inside the ../stories/index.js file, like this:
import React from 'react';
import { storiesOf } from '@storybook/react';
import { Button } from '@storybook/react/demo';
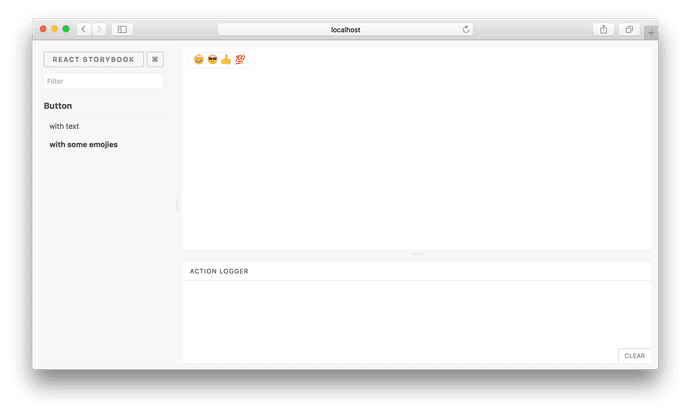
storiesOf('Button', module)
.add('with text', () => <Button>Hello Button</Button>)
.add('with some emoji', () => (
<Button>
<span role="img" aria-label="so cool">
😀 😎 👍 💯
</span>
</Button>
));
Each story is a single state of your component. In the above case, there are two stories for the demo button component:
- With text
- With some emoji
Run your Storybook
Now everything is ready. Run your storybook with:
npm run storybook
Then you can see all your stories, like this:
Now you can change components and write stories whenever you need to. You’ll see the changes in Storybook immediately since it uses Webpack’s hot module reloading.